This is Part 4 of the 7-part Exercise 6-0. Click here to see the other parts.
Exercise 6-0 (Part 4 / 7)
Relating to section 6.1.3 of the textbook (page 105-109). Implement and test out the “Finding URLs” program. The program scans a line of input text, and automatically detect and display all the URL addresses within that line of text.
The Project
This section summarises the partitioned program in the form of C++ source and header files.
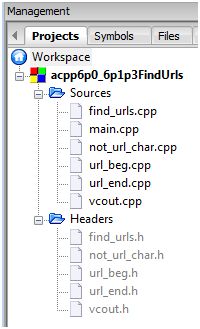
Source File List
Header File List
Source Files
main.cpp
#include <iostream> // cin, cout, endl
#include <string> // string
#include <vector> // vector
#include "find_urls.h" // find_url
#include "vcout.h" // vcout
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::vector;
int main()
{
cout << "Enter a line. This program automatically find URLs..." << endl;
// Read a line of input, then find and display URLs.
string line;
vector<string> urls;
while (getline(cin, line)) {
vector<string> urls = find_urls(line);
vcout(urls);
}
return 0;
}
find_urls.cpp
#include <string> // string
#include <vector> // vector
#include "url_beg.h" // url_beg
#include "url_end.h" // url_end
using std::string;
using std::vector;
vector<string> find_urls(const string& s)
{
vector<string> ret;
typedef string::const_iterator iter;
iter b = s.begin(), e = s.end();
// look through the entire input
while (b != e) {
// look for one or more letters followed by ://
b = url_beg(b, e);
// if we found it
if (b != e) {
// get the rest of the URL
iter after = url_end(b, e);
// remember the URL
ret.push_back(string(b, after));
// advance b and check for more URLs on this line
b = after;
}
}
return ret;
}
not_url_char.cpp
<br />#include <string> // string, isalnum
#include <algorithm> // find
using std::string;
bool not_url_char(char c)
{
// characters, in addition to alphanumerics, that can appear in a URL
static const string url_ch = "~;/?:@=&$-_.+!*'(),";
// see whether c can appear in a URL and return the negative
return !(isalnum(c) || find(url_ch.begin(), url_ch.end(), c) != url_ch.end() );
}
url_beg.cpp
#include <string> // string, isalpha
#include <algorithm> // search
#include "not_url_char.h" // not_url_char
using std::string;
string::const_iterator
url_beg(string::const_iterator b, string::const_iterator e)
{
static const string sep = "://";
typedef string::const_iterator iter;
// i marks where the separator was found
iter i = b;
while ((i = search(i, e, sep.begin(), sep.end() )) != e) {
// make sure the separator isn't at the beginning or end of the line
if (i != b && i + sep.size() != e) {
// beg marks the beginning of the protocol-name
iter beg = i;
while (beg != b && isalpha(beg[-1]))
--beg;
// is there at least one appropriate character before and after the separator?
if (beg != i && !not_url_char(i[sep.size()]))
return beg;
}
// the separator we found wasn't part of a URL; advance i past this separator
i += sep.size();
}
return e;
}
url_end.cpp
#include <string> // string
#include <vector> // vector
#include <algorithm> // find_if
#include "not_url_char.h" // not_url_char
using std::string;
string::const_iterator
url_end(string::const_iterator b, string::const_iterator e)
{
return find_if(b, e, not_url_char);
}
vcout.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // string
#include <vector> // vector
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::vector;
int vcout(const vector<string>& v)
{
for (vector<string>::const_iterator i = v.begin(); i != v.end(); ++i)
cout << (*i) << endl;
return 0;
}
Header Files
find_urls.h
#ifndef GUARD_FIND_URLS_H #define GUARD_FIND_URLS_H #include <vector> #include <string> std::vector<std::string> find_urls(const std::string&); #endif // GUARD_FIND_URLS_H
not_url_char.h
#ifndef GUARD_NOT_URL_CHAR_H #define GUARD_NOT_URL_CHAR_H bool not_url_char(char); #endif // GUARD_NOT_URL_CHAR_H
url_beg.h
#ifndef GUARD_URL_BEG_H #define GUARD_URL_BEG_H std::string::const_iterator url_beg(std::string::const_iterator, std::string::const_iterator); #endif // GUARD_URL_BEG_H
url_end.h
#ifndef GUARD_URL_END_H #define GUARD_URL_END_H #include <string> std::string::const_iterator url_end(std::string::const_iterator, std::string::const_iterator); #endif // GUARD_URL_END_H
vcout.h
#ifndef GUARD_VCOUT_H #define GUARD_VCOUT_H #include <string> #include <vector> int vcout(const std::vector<std::string>&); #endif // GUARD_VCOUT_H
Test program
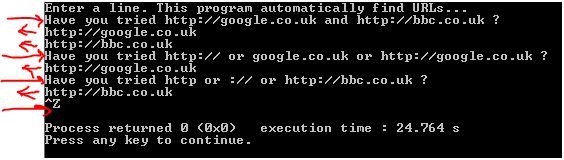
Let’s do some simple tests:
- Submitting the line “Have you tried http://google.co.uk and http://bbc.co.uk ?”, the program should return: “http://google.co.uk” and “http://bbc.co.uk”.
- Submitting the line “Have you tried http:// or google.co.uk or http://google.co.uk ?”, the program should return: “http://google.co.uk”.
- Submitting the line “Have you tried http or :// or http://bbc.co.uk ?”, the program should return: “http://bbc.co.uk “.