The Background
Under normal circumstances, we can download a program from the internet, followed by the standard Windows installation procedure. In otherwords, from downloading to installing to using the program, it is a matter of a few clicks. (The computer “sorts it out” for us).
The Challenge
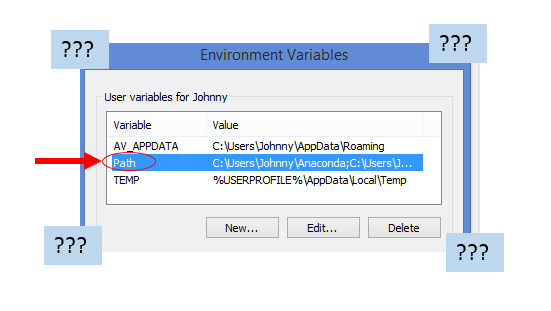
Recently I have to manually install programs on my Windows 8.1. i.e. Download a ZIP file (to the local Windows download directory), extract it, and store the executables “somewhere” on the computer. Once installed to that “somewhere”, we need to append the path-name to the Environmental variable PATH so that Windows knows where to call it from when we invoke the executable (.exe file).
The Solution / Inspiration
This YouTube video (FFMPEG: Installing FFMPEG On Windows) has inspired me an easy way to organize these manual Installs.
Organize my Manual Installs
To keep things tidy I have formulated my own little “standard” (I will just have to stick to it for a while to see if it is a good standard or not!):
- create
c:\my_bins. - inside this
my_binsdirectory, create a folder for each manual-installed programs. (e.g.youtube-dl,ffmpeg, etc.) - inside the program folder (e.g.
C:\my_bins\ffmpeg), copy and paste the files to here. - ideally, the
.exefiles will be under a folder calledbin. e.g. insideC:\my_bins\ffmpeg\binit may contains a bunch of.exefiles which we wish to call from command prompts / Git Bash. - append the search path to the
PATHuser environmental variable. e.g.C:\my_bins\ffmpeg\bin. - restart the command prompt (or Git Bash). We should now be able to call the executables (the programs) directly – from anywhere of the file system.
Conclusion
This post summarizes a formula that I use to organize manual-installed programs, on Windows machine. (I believe similar principles may also be applied to other platforms / operating systems.